
PROGNOSTIC VS PREDICTIVE SKIN
The severity of EGFR mAbs-cetuximab and panitumumab induced skin rashes is associated with a better response to these treatments, although, its predictive role is not established in HNSCC patients.
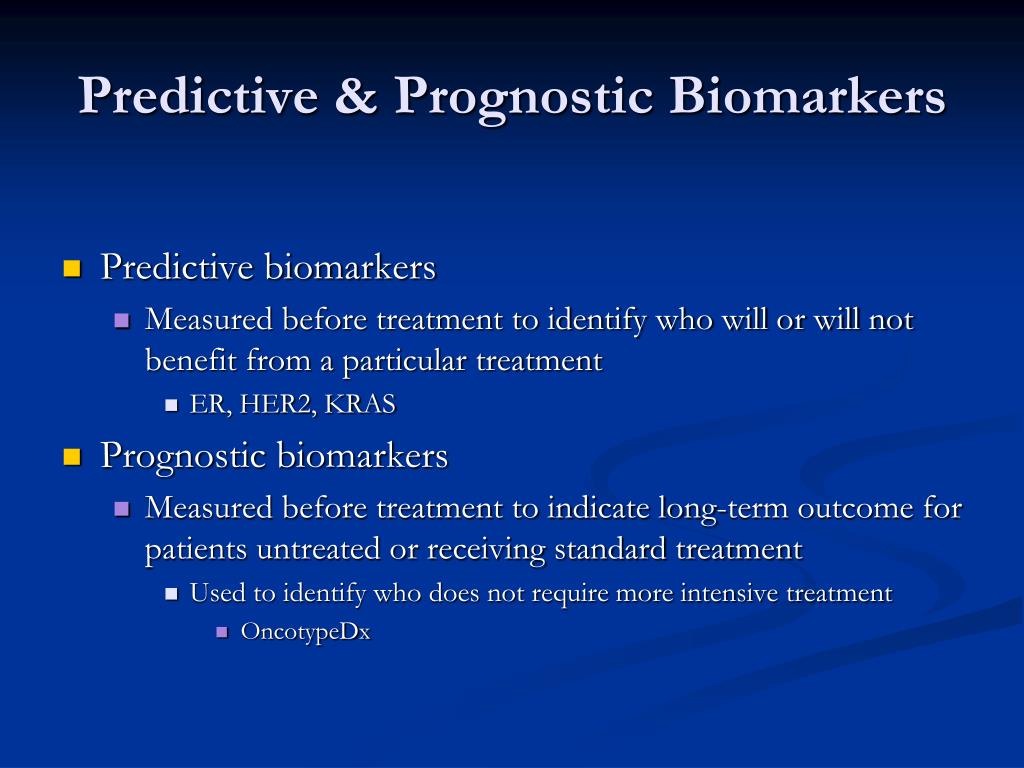
EGFR protein expression and gene amplification are not useful to predict response to EGFR mAbs in HNSCC patients, as shown by our previous study and others. Currently, there are no established biomarkers for predicting treatment response to these therapies. Thus, it is necessary to identify patients most likely to benefit from these treatments. EGFR-targeted therapies are only marginally effective, expensive and often associated with toxicity. At present, due to the lack of predictive biomarkers in HNSCC, these therapies are offered indiscriminately to patients leading to a poor benefit to risk ratio. However, unlike non-small cell lung cancer and colorectal cancer, their clinical use in treatment decision making is yet to be established. Resistance mechanisms for anti-EGFR therapies in HNSCCs are reported in the literature including high expression of EGFR ligands, HER3, Src family kinases and HGF/MET axis. In addition, recent data suggest that EGFR targeting in combination with radiation is not an acceptable substitute for cisplatin-radiation in human papillomavirus (HPV)-positive HNSCC patients. However, the addition of an EGFR-targeting monoclonal antibody (mAb) to radiation or chemoradiation therapy has shown limited success. The only targeted therapy approved for LA-HNSCC patients by the Food and Drug Administration is that against EGFR. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression occurs in >80% of HNSCC tumours and is a hallmark of HNSCCs. Patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) frequently present with locally advanced (LA) primary disease with concurrent chemoradiation as the standard treatment of care.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
